Problematic References Is Highly Prevalent among Scientific Publications
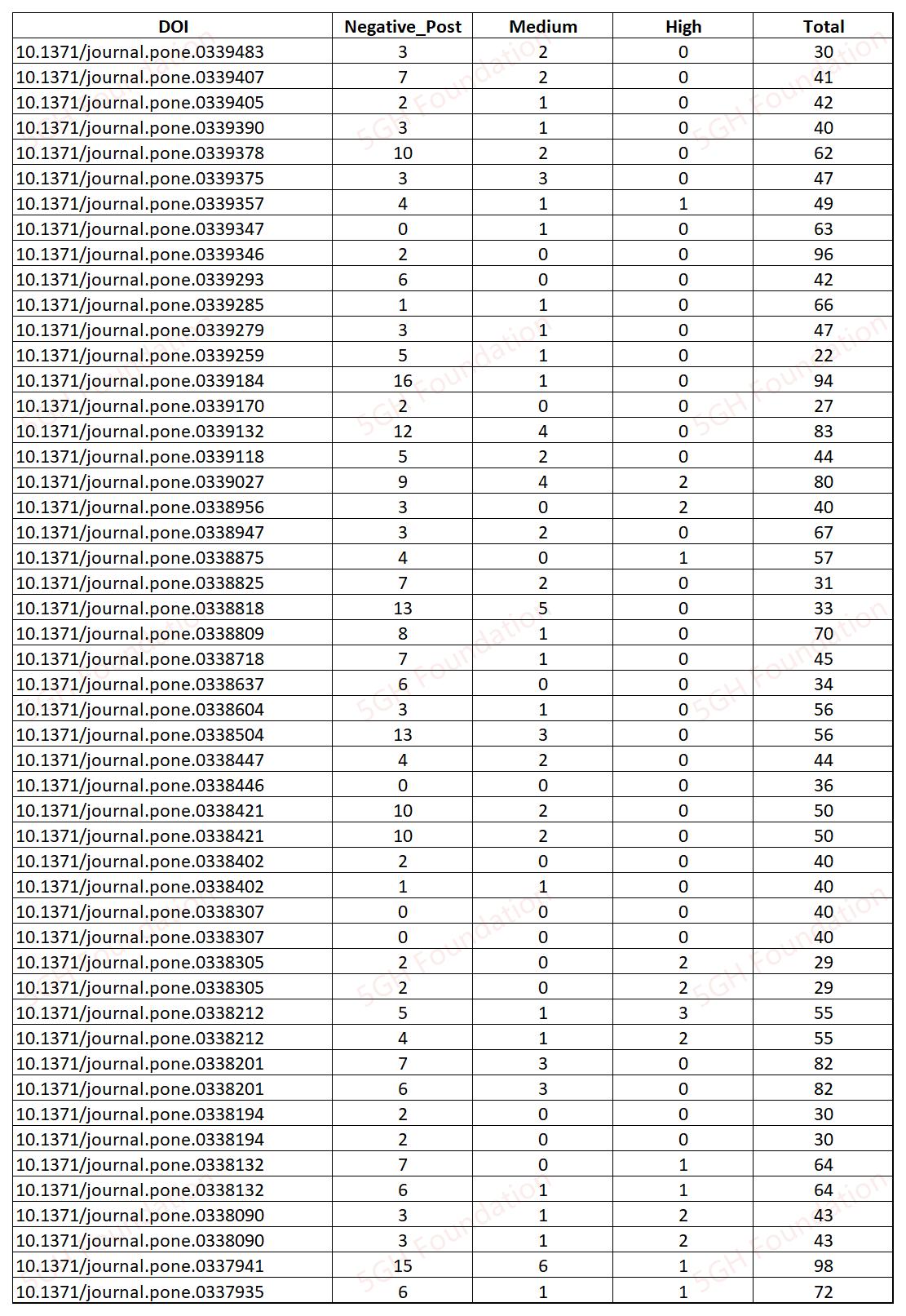
The 5GH Team analyzed the 50 most recently published articles on PLoS ONE using "RetractionRisk Scanner", a tool developed by Mr ZHENG Erte and his colleagues, and identified problematic references in 48 out of these 50 articles.
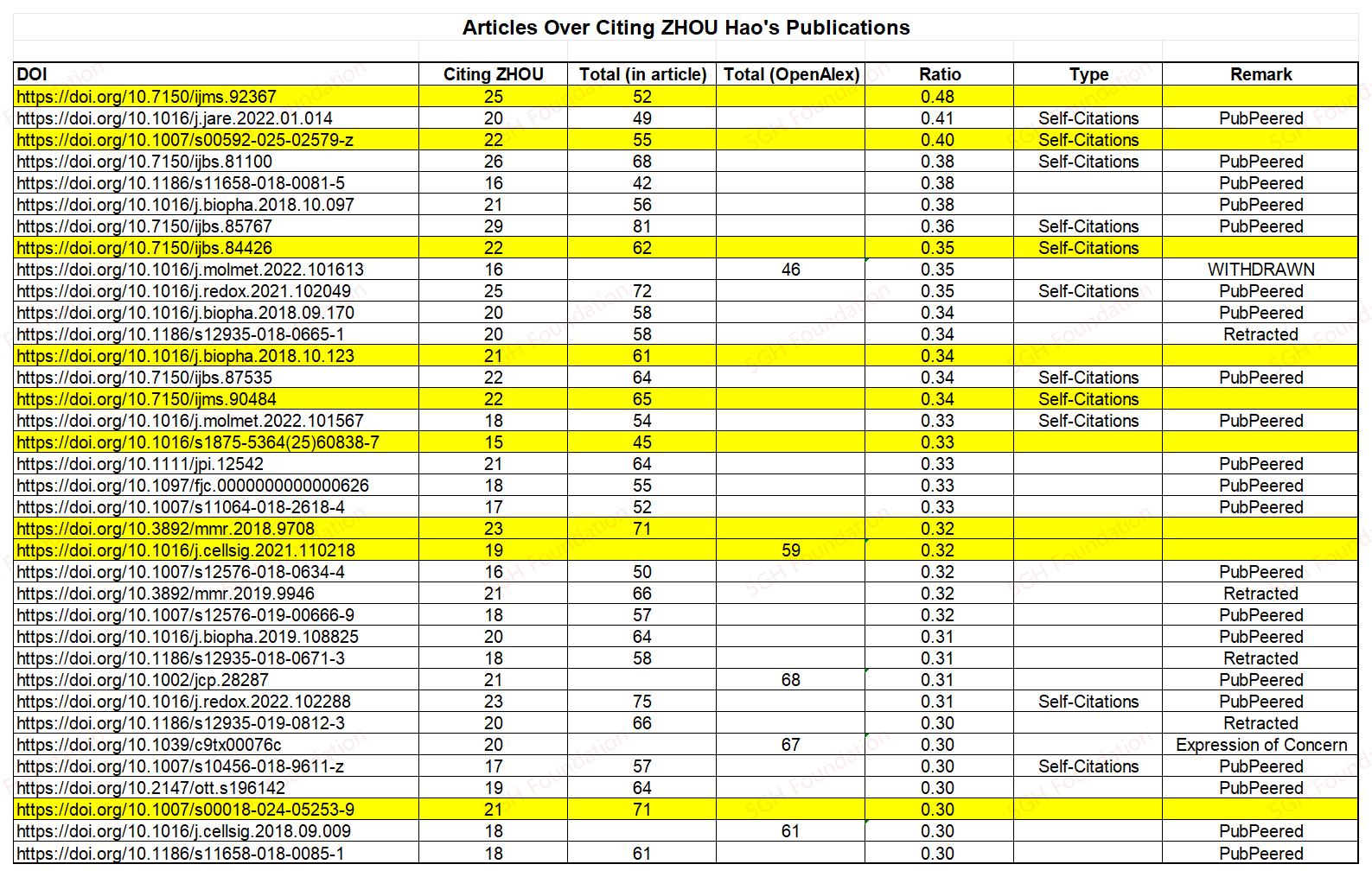
"RetractionRisk Scanner" assesses the risk of being retracted on every reference based on PubPeer comments and the social media posts on the references, as well as other factors. In our analysis, "problematic references" are those having negative PubPeer or social media posts, or those being classified to be Medium/High Risk by "RetractionRisk Scanner".
The results form our analysis are shocking. About 96% (48/50) of the most recently published articles on PLoS ONE have "problematic" references. Specifically, 46 articles have references with negative PubPeer or social media posts, 35 articles have "Medium Risk" references, and 14 articles have "High Risk" references.
The 5GH addresses that the current analysis is a primary investigation, limitations should be acknowledged. The methodology of "RetractionRisk Scanner" has not undergone peer review, and thus the reliability of its assessments should be interpreted with caution. Notably, many references were flagged as being associated with negative social media posts, but such attributions are often found to be inaccurate. And it is not true that all of those problematic citations resulted from misbehaviour in the publications of those articles.
This analysis was not targeting PLoS ONE and its publisher. Rather, the publisher's commitment to open science has greatly facilitated our access to article content. A plan to extend our recent analysis is currently underway.