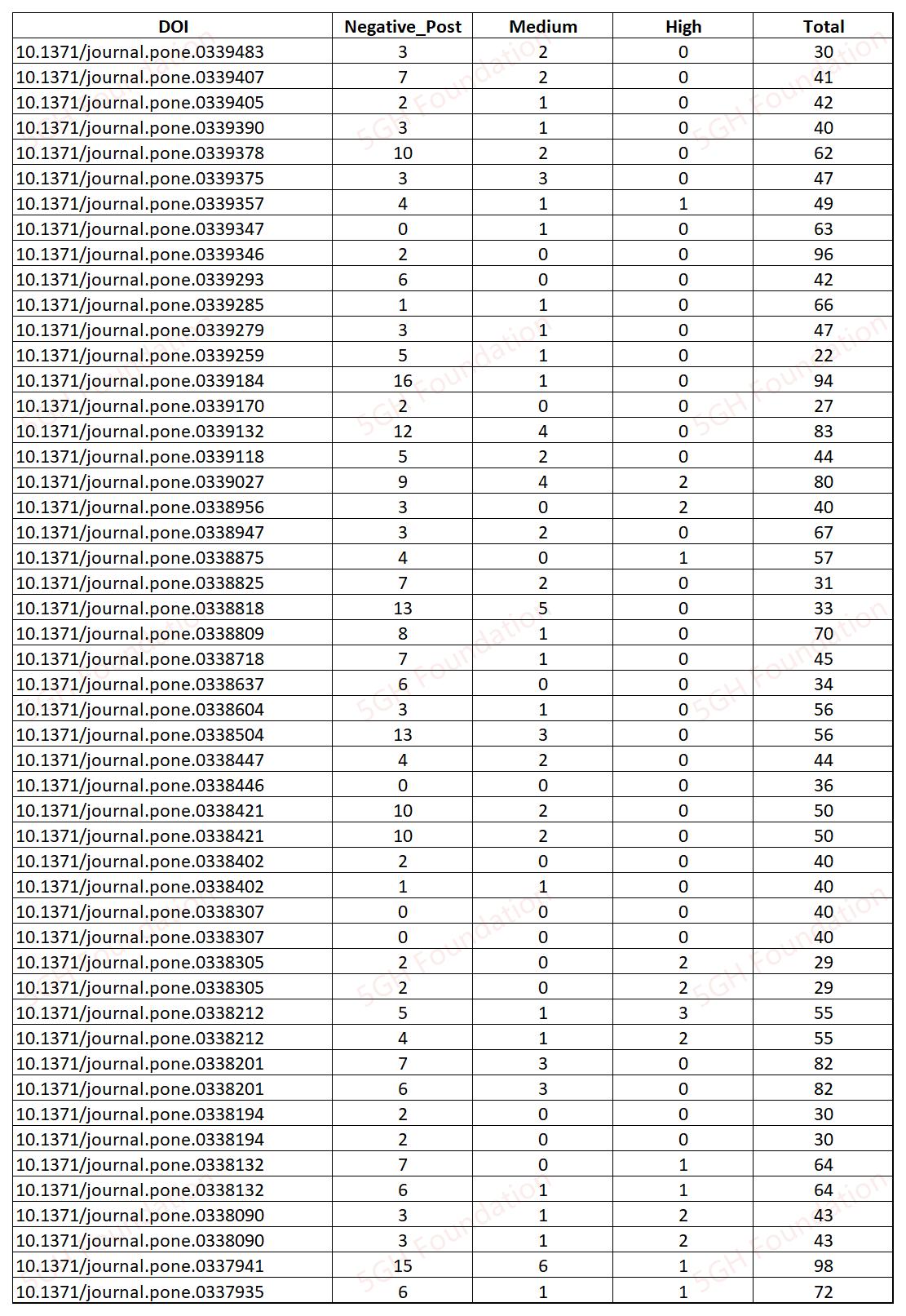
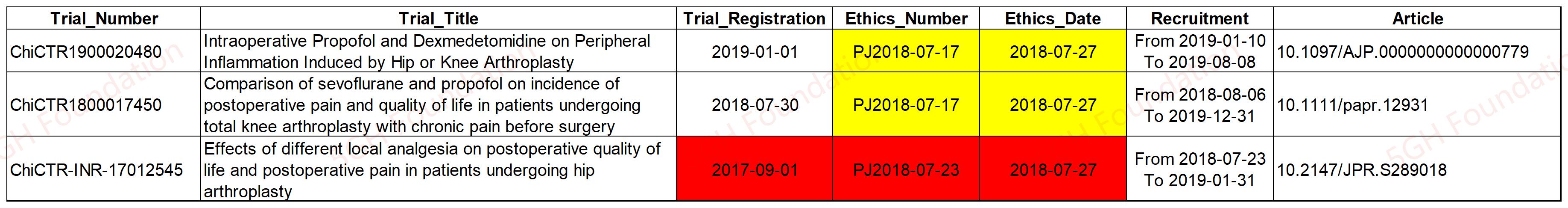
Reused Images on 10.1016/j.psep.2024.03.026
Reused images are observed on the article [1].
The SEM images on Figure 2 (a), (b), and (c) were described to be taken from different samples, (a) and (b) were taken from "mesoporous inorganic silica", but (d) were taken from "organic ligand-modified composite adsorbent", however, the images on Figure 2 (a), (b), and (c) are identical to each other.
Reference